PowerBI data source
Power Query
Power Query is the data source editor in PowerBI.
On PowerBI Desktop, within a report, click on Transform Data. This will open Power Query and allow us to configure the data source.
Here you can configure which data you want to retrieve, set field types, etc.
Creating the Data Source
To add our source, click on New Source then Blank Query.
In the formula bar, enter the following:
= Table.PromoteHeaders(
Csv.Document(
Web.Contents(
"https://api.cadulis.com/data-sources/export-excel/[CODE_CADULIS].csv",
[Headers=[#"Accept-Encoding"="gzip"]]
)
)
)
You must replace
[CODE_CADULIS]in the code above with your own data source identifier.This is the identifier obtained in the Prerequisites section.
Sample Data
You can use our sample data source:
https://api.cadulis.com/data-sources/export-excel/XXXXXXXXXXinterventionsXXXXX.csv
Use the URL above and you will get some sample data to practice with!
.csv Format
You should see something like this:
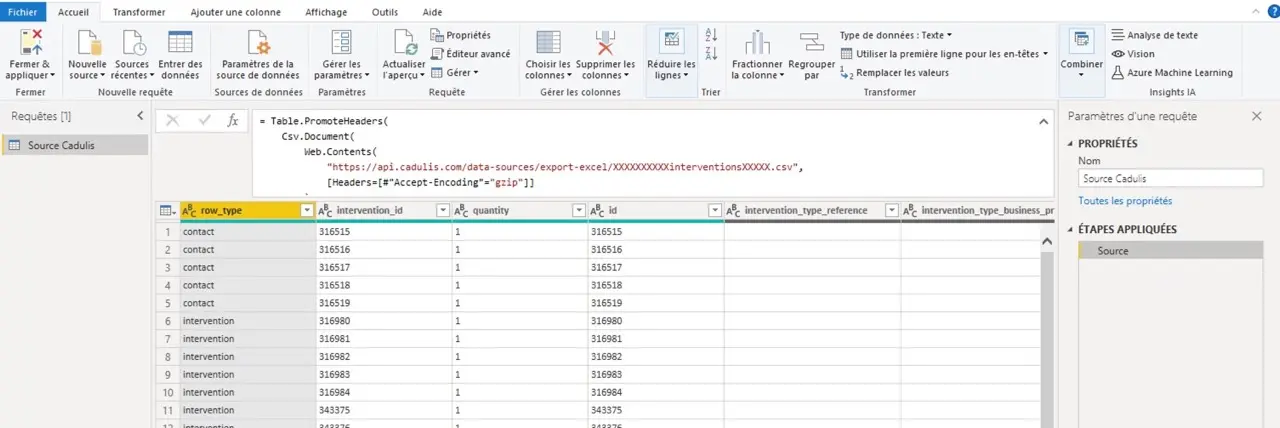
Power Query displays the first few rows of your data source.
Column Types
We need to tell PowerBI that certain columns are of type whole number, decimal number, or date. This will make it easier to work with the data and enable calculations.
On the right side, in the steps section, right-click on the first step and select Add Step After.
Enter the following in the step’s code:
= Table.TransformColumnTypes(
Source, {
{"intervention_id", Int64.Type},
{"id", Int64.Type},
{"intervention_type_id", Int64.Type},
{"business_unit_id", Int64.Type},
{"intervention_parent_id", Int64.Type},
{"created_at", type datetime},
{"scheduled_start_at", type datetime},
{"scheduled_end_at", type datetime},
{"start_at", type datetime},
{"end_at", type datetime},
{"report_at", type datetime},
{"intermediate_report_at", type datetime},
{"updated_at", type datetime},
{"with_appointment", Int64.Type},
{"intervention_container_id", Int64.Type},
{"self_service", Int64.Type},
{"self_service_start_at", type datetime},
{"ignore_restriction", Int64.Type},
{"customer.id", Int64.Type},
{"financial.drive_distance", type number},
{"financial.price_fees", type number},
{"financial.total_price", type number},
{"financial.price", type number},
{"financial.cost_fees", type number},
{"financial.total_cost", type number},
{"financial.cost", type number},
{"financial.drive_duration", type number},
{"accounting.billable", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.billable_transmitted", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.billed", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.payment_sent", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.invoiceable", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.invoiceable_transmitted", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.invoiced", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.payment_received", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.billable_amount", type number},
{"accounting.billed_amount", type number},
{"accounting.payment_sent_amount", type number},
{"accounting.invoiceable_amount", type number},
{"accounting.invoiced_amount", type number},
{"accounting.payment_received_amount", type number},
{"driving.distance_before", type number},
{"driving.distance_after", type number},
{"driving.duration_before", type number},
{"driving.duration_after", type number},
{"driving.distance_total", type number},
{"driving.duration_total", type number},
{"location.latitude", type number},
{"location.longitude", type number},
{"location.accuracy", Int64.Type}
})
You will get the following:
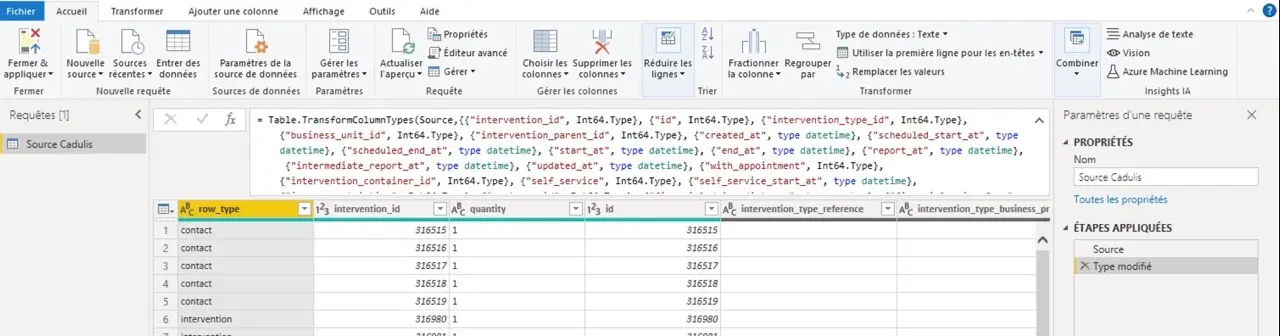
Feel free to revisit your data source when you add custom fields:
By specifying the type of your columns to PowerBI, you enable it to better understand your data, speed up comparisons, and allow calculations.
Click the Close & Apply button in the top left.





