Fuente de datos PowerBI
Power Query
Power Query es el editor de fuentes de datos en PowerBI.
En PowerBI Desktop, dentro de un informe, haz clic en Transformar datos. Esto abrirá Power Query y te permitirá configurar la fuente de datos.
Aquí es donde puedes configurar qué datos quieres recuperar, tipar los campos, etc.
Creación de la fuente de datos
Para agregar nuestra fuente, haz clic en Nueva fuente y luego en Consulta en blanco.
En el cuadro para ingresar la fórmula, indica lo siguiente:
= Table.PromoteHeaders(
Csv.Document(
Web.Contents(
"https://api.cadulis.com/data-sources/export-excel/[CODE_CADULIS].csv",
[Headers=[#"Accept-Encoding"="gzip"]]
)
)
)
Debes reemplazar en el código anterior
[CODE_CADULIS]por tu propio identificador de fuente de datos.Es el identificador obtenido en la sección Prerrequisitos
Datos de ejemplo
Puedes utilizar nuestra fuente de datos de ejemplo:
https://api.cadulis.com/data-sources/export-excel/XXXXXXXXXXinterventionsXXXXX.csv
¡Utiliza esta URL y tendrás directamente algunos datos para practicar!
Formato .csv
Deberías tener algo parecido a esto:
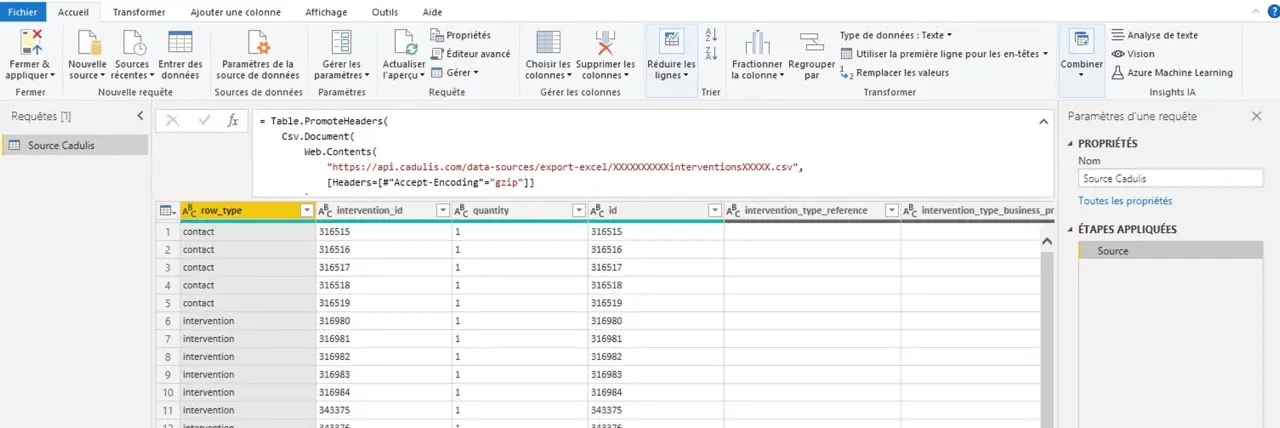
Power Query te muestra las primeras líneas de tu fuente de datos.
Tipo de las columnas
Necesitamos indicarle a PowerBI que ciertas columnas son de tipo número entero, número decimal o fecha. Esto permitirá navegar mejor por los datos y poder realizar cálculos.
En la parte derecha, en los pasos, haz clic derecho sobre el primer paso y selecciona Agregar paso después.
Indica lo siguiente en el código del paso:
= Table.TransformColumnTypes(
Source, {
{"intervention_id", Int64.Type},
{"id", Int64.Type},
{"intervention_type_id", Int64.Type},
{"business_unit_id", Int64.Type},
{"intervention_parent_id", Int64.Type},
{"created_at", type datetime},
{"scheduled_start_at", type datetime},
{"scheduled_end_at", type datetime},
{"start_at", type datetime},
{"end_at", type datetime},
{"report_at", type datetime},
{"intermediate_report_at", type datetime},
{"updated_at", type datetime},
{"with_appointment", Int64.Type},
{"intervention_container_id", Int64.Type},
{"self_service", Int64.Type},
{"self_service_start_at", type datetime},
{"ignore_restriction", Int64.Type},
{"customer.id", Int64.Type},
{"financial.drive_distance", type number},
{"financial.price_fees", type number},
{"financial.total_price", type number},
{"financial.price", type number},
{"financial.cost_fees", type number},
{"financial.total_cost", type number},
{"financial.cost", type number},
{"financial.drive_duration", type number},
{"accounting.billable", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.billable_transmitted", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.billed", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.payment_sent", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.invoiceable", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.invoiceable_transmitted", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.invoiced", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.payment_received", Int64.Type},
{"accounting.billable_amount", type number},
{"accounting.billed_amount", type number},
{"accounting.payment_sent_amount", type number},
{"accounting.invoiceable_amount", type number},
{"accounting.invoiced_amount", type number},
{"accounting.payment_received_amount", type number},
{"driving.distance_before", type number},
{"driving.distance_after", type number},
{"driving.duration_before", type number},
{"driving.duration_after", type number},
{"driving.distance_total", type number},
{"driving.duration_total", type number},
{"location.latitude", type number},
{"location.longitude", type number},
{"location.accuracy", Int64.Type}
})
Obtendrás esto:
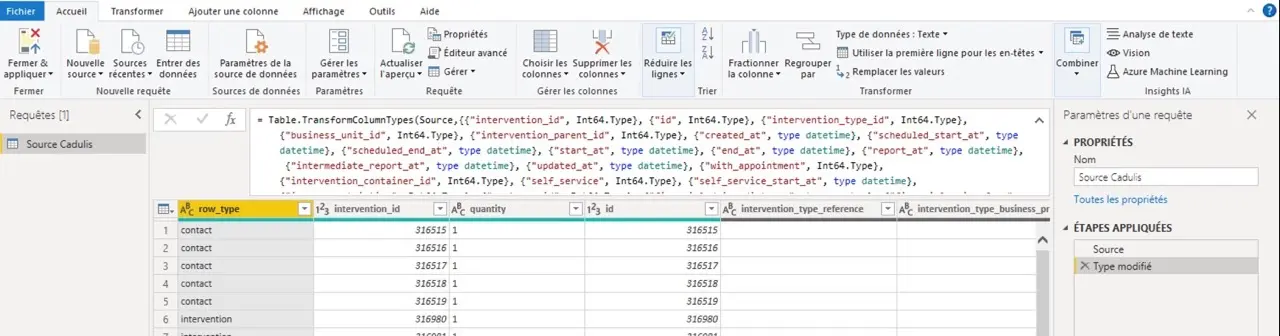
No dudes en volver a tu fuente de datos cuando agregues campos personalizados:
al especificar a PowerBI el tipo de tus columnas, le permitirás comprender mejor tus datos, acelerar las comparaciones y habilitar los cálculos.
Haz clic en el botón en la parte superior izquierda Cerrar y aplicar.





